Digestive Health: Probiotics and Gut-Friendly Products dives deep into the fascinating world of gut health. From understanding the crucial role of probiotics in supporting digestion to exploring a variety of gut-friendly foods, this guide unlocks the secrets to a healthier gut microbiome. We’ll uncover how a balanced diet, stress management, and lifestyle choices all impact your digestive system. Get ready to explore the power of probiotics and discover how to nourish your gut for optimal well-being.
This comprehensive guide explores the mechanisms behind probiotics, comparing different strains and highlighting the importance of quality products. We’ll also delve into gut-friendly foods, exploring prebiotics and fermented foods, and revealing how these foods can boost gut health. Furthermore, we’ll examine the diverse benefits of probiotics and gut-friendly products, including improved digestion, immunity, and even mental well-being. You’ll also learn how to choose the right probiotics, understand potential side effects, and make informed decisions for optimal gut health.
Introduction to Digestive Health
Your gut isn’t just a dumping ground; it’s a powerhouse of health! Digestive health plays a crucial role in everything from nutrient absorption to mood regulation, impacting your overall well-being in profound ways. A healthy gut means a happy you, and understanding the factors that influence it is key to feeling your best.
A balanced digestive system is essential for extracting the nutrients your body needs from food, converting them into energy, and eliminating waste effectively. This intricate process directly impacts your energy levels, immunity, and even your mental clarity. A well-functioning gut is your body’s support system, working tirelessly to keep you running smoothly.
The Importance of Gut Health
Digestive health isn’t just about avoiding stomach aches; it’s about supporting your body’s intricate system. A healthy gut fosters a robust immune system, helping you fight off illnesses more effectively. It also plays a vital role in nutrient absorption, ensuring your body gets the building blocks it needs to function optimally. Research consistently highlights the link between gut health and mental well-being, demonstrating that a healthy gut can positively influence mood and reduce feelings of anxiety and stress.
Factors Impacting Digestive Health
Several factors influence your digestive health, making it a complex interplay of choices and circumstances. Diet, stress, and lifestyle choices all contribute to the overall health of your gut.
- Diet: A diet rich in processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of unhealthy fats can disrupt the delicate balance of gut bacteria. Conversely, a diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods can nourish your gut microbiome and support a healthy digestive system. Consider incorporating foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi for their probiotic content.
- Stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact the gut’s delicate ecosystem, potentially leading to digestive issues like bloating, cramping, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Stress management techniques like meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature can help mitigate these effects.
- Lifestyle: Factors like sleep deprivation, lack of physical activity, and excessive alcohol consumption can also negatively affect digestive health. Prioritizing regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and a balanced approach to alcohol consumption can support a healthy gut.
The Role of Probiotics in Supporting Digestion
Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, offer health benefits. They play a vital role in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, which is the community of microorganisms residing in your digestive tract. This community is crucial for digestion, immunity, and overall well-being.
“A healthy gut microbiome is essential for proper digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function.”
A Brief History of Probiotics, Digestive Health: Probiotics and Gut-Friendly Products
The concept of probiotics dates back centuries, with early civilizations recognizing the benefits of fermented foods for health. Ancient practices involved consuming fermented dairy products, like yogurt and kefir, and these traditions laid the groundwork for modern probiotic research. Early research focused on the specific microorganisms in these foods and their potential benefits. Modern science has since identified and studied various probiotic strains, further solidifying their role in digestive health.
Types of Probiotics and Their Benefits
Different types of probiotics offer varied benefits.
| Probiotic Strain | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Lactobacillus acidophilus | Improved digestion, reduced lactose intolerance, and enhanced immune function |
| Bifidobacterium spp. | Improved digestion, reduced bloating, and potentially enhanced mood |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus | Improved digestion, reduced diarrhea, and enhanced immune response |
| Saccharomyces boulardii | Reduced diarrhea, particularly associated with antibiotic use, and improved gut barrier function |
Understanding Probiotics: Digestive Health: Probiotics And Gut-Friendly Products
Probiotics, those beneficial bacteria touted for gut health, are more than just a trendy buzzword. They’re live microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, offer a plethora of benefits for your digestive system. Understanding how they work and the types available can empower you to make informed choices about your health.
Probiotics work by establishing a balance within your gut microbiome, which is a complex ecosystem of bacteria. They compete with harmful bacteria for resources, potentially reducing their ability to thrive. This balanced environment promotes better digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall gut health. Their impact extends beyond the digestive tract, potentially affecting immune function and even mental well-being.
Mechanisms of Probiotic Action
Probiotics exert their influence through several mechanisms. They produce substances that inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria, creating a hostile environment for them. They also stimulate the immune system, leading to a more robust defense against pathogens. Finally, they promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, further enhancing the gut’s overall health.
Types of Beneficial Bacteria in Probiotics
Numerous strains of bacteria are used in probiotic products. Common types include *Lactobacillus* and *Bifidobacterium*. *Lactobacillus* species, such as *L. acidophilus* and *L. rhamnosus*, are known for their ability to produce lactic acid, creating an acidic environment that inhibits harmful bacteria. *Bifidobacterium* species, like *B. bifidum* and *B. longum*, are crucial for maintaining gut health and have diverse roles in the digestive process. Other beneficial bacteria, like *Streptococcus thermophilus*, are also found in certain probiotic formulations.
Effectiveness of Different Probiotic Strains
The effectiveness of different probiotic strains can vary. Some strains show stronger evidence of improving specific digestive issues, such as *Lactobacillus* strains for lactose intolerance or *Bifidobacterium* for diarrhea. Research continues to explore the nuanced effects of different strains, and results are often dependent on the specific strain, the individual’s gut microbiome, and the duration of consumption. It’s essential to remember that not all strains are equally effective for everyone.
Choosing High-Quality Probiotic Products
Selecting high-quality probiotic products is crucial for maximizing benefits. Look for products that specify the exact strains of bacteria present and their quantities. A high CFU (colony-forming units) count indicates a greater number of live bacteria, which is generally desirable. Reputable brands and third-party certifications can offer assurance of product quality and safety. Be wary of products with vague or unsubstantiated claims.
Potential Side Effects of Probiotics
While generally safe, probiotics can sometimes cause mild side effects. These are usually temporary and resolve on their own. Potential side effects include bloating, gas, and diarrhea. Individuals with compromised immune systems or underlying health conditions should consult a healthcare professional before taking probiotics.
| Potential Side Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Bloating | A feeling of fullness or distension in the abdomen. |
| Gas | The production of excessive intestinal gas. |
| Diarrhea | Frequent bowel movements with loose or watery stools. |
| Headache | Pain in the head. |
| Nausea | A feeling of discomfort in the stomach, often accompanied by the urge to vomit. |
Forms of Probiotics
Probiotics are available in various forms, including capsules, powders, and gummies. Capsules offer a convenient way to consume probiotics, while powders can be mixed into beverages or foods. Gummies are a popular option for children or those who prefer a palatable form. Liquid forms are also available, though their stability can sometimes be a concern.
Gut-Friendly Products
Your gut is your second brain, and what you feed it directly impacts your overall well-being. From mood swings to skin issues, a happy gut ecosystem can drastically improve your quality of life. Understanding which foods nurture your gut microbiome is key to unlocking this inner harmony. Today, we’re diving into the world of gut-friendly products, exploring how specific foods support a thriving gut and the fantastic benefits they offer.
Gut-friendly foods are more than just a trendy diet buzzword; they’re essential for maintaining a balanced and robust gut microbiome. This diverse community of bacteria plays a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, immune function, and even mental health. Choosing foods that nourish these beneficial bacteria can significantly enhance your gut health and overall well-being.
Understanding Gut-Friendly Foods
Gut-friendly foods are those rich in prebiotics and probiotics, essential components for supporting a healthy gut microbiome. Prebiotics act as food for the beneficial bacteria, while probiotics are the beneficial bacteria themselves. A diet rich in these foods can lead to a more diverse and balanced gut flora, contributing to improved digestion, enhanced immunity, and overall well-being.
Foods That Promote Gut Health
A plethora of foods can contribute to a healthy gut. These foods are not just tasty but also packed with nutrients that nurture the beneficial bacteria in your gut.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Fruits and vegetables are a cornerstone of a healthy diet, providing essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Fiber is a crucial prebiotic, feeding the good bacteria in your gut and promoting regular bowel movements. Think berries, leafy greens, and colorful vegetables like carrots and broccoli.
- Legumes: Legumes like beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of fiber, which acts as a prebiotic, stimulating the growth of beneficial bacteria in your gut. They also provide protein and essential nutrients, making them a valuable addition to any diet.
- Whole Grains: Whole grains, like brown rice, quinoa, and oats, are rich in fiber, which acts as a prebiotic, supporting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. Their complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy and promote healthy digestion.
The Role of Prebiotics
Prebiotics are non-digestible food ingredients that selectively stimulate the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria in the colon. They are essentially food for the probiotics, fostering a healthy gut environment. A diet rich in prebiotics ensures that beneficial bacteria thrive, promoting overall gut health.
Fermented Foods Rich in Probiotics
Fermented foods are a fantastic source of probiotics, live microorganisms that offer numerous benefits for gut health. These foods, through a natural fermentation process, introduce beneficial bacteria directly into the gut. Examples include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha.
- Yogurt: A staple in many diets, yogurt contains live and active cultures of beneficial bacteria, like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. These probiotics aid digestion, boost immunity, and improve gut health.
- Kefir: Similar to yogurt, kefir is a fermented milk drink containing a diverse range of probiotics. It is often considered a more potent probiotic source than yogurt, offering a wide array of benefits for gut health.
- Sauerkraut and Kimchi: These fermented cabbage and vegetables, respectively, are rich in probiotics, supporting digestion and gut health. They also offer a unique blend of flavors and textures, making them a delicious addition to meals.
- Kombucha: This fermented tea beverage contains a variety of probiotics, contributing to a healthy gut environment. It offers a unique and refreshing taste experience while supporting digestive well-being.
Benefits of Incorporating Gut-Friendly Products
Incorporating gut-friendly products into your diet offers a wide range of benefits. Improved digestion, enhanced nutrient absorption, a strengthened immune system, and even improved mood are just some of the potential benefits.
Gut-Friendly Foods and Probiotic Content
| Food | Probiotic Content (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Yogurt | High |
| Kefir | Very High |
| Sauerkraut | Moderate |
| Kimchi | Moderate |
| Kombucha | Low |
| Fruits and Vegetables | Low to Moderate (depending on type) |
| Legumes | Low |
| Whole Grains | Low |
Benefits of Probiotics and Gut-Friendly Products

Source: foodrevolution.org
Taking care of your gut health is totally key, and that often means choosing probiotic-rich foods and gut-friendly products. But did you know that many of these awesome products are also surprisingly eco-friendly? Check out The Best Eco-Friendly Products for Everyday Life for some seriously cool, sustainable options that are good for your insides and the planet.
From reusable water bottles to compostable food containers, these products can totally boost your digestive health journey. So, next time you’re stocking up on probiotics, look for eco-friendly alternatives—it’s a win-win!
Your gut, a bustling ecosystem of trillions of microorganisms, plays a crucial role in your overall health. Beyond digestion, the gut microbiome impacts your immune system, mental well-being, and even your risk of chronic diseases. Probiotics and gut-friendly products offer a way to nourish this vital community, potentially unlocking a range of health benefits.
Probiotics are live microorganisms, often bacteria or yeasts, that offer a multitude of advantages when consumed regularly. Gut-friendly foods, naturally rich in beneficial microbes or prebiotics that feed these microbes, complement probiotic supplements. These foods and supplements contribute to a healthy gut microbiome, a complex community of microorganisms that influences many aspects of your health.
Improved Digestion
A healthy gut microbiome is fundamental to efficient digestion. Probiotics support the breakdown of food, aiding in the absorption of nutrients and preventing digestive issues like bloating, gas, and constipation. This enhanced digestion leads to better nutrient absorption and a more comfortable digestive experience. For example, certain probiotics are known to produce enzymes that aid in lactose digestion, making dairy products more easily tolerated for individuals with lactose intolerance.
Immune System Support
The gut is closely linked to the immune system. A healthy gut microbiome can strengthen the immune response, protecting against infections and allergies. Probiotics can stimulate the production of beneficial immune cells, potentially reducing the risk of illness. For instance, research suggests that regular consumption of probiotics can help reduce the frequency and severity of respiratory infections.
Mental Well-being
Emerging research suggests a connection between the gut microbiome and mental health. The gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication pathway between the gut and the brain, plays a significant role in mood regulation and cognitive function. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome through probiotics might positively influence mental well-being, potentially reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Nutrient Absorption
Gut bacteria play a crucial role in nutrient absorption. They produce enzymes that help break down complex carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into absorbable forms. These nutrients are then utilized by the body for energy, growth, and repair. A balanced gut microbiome ensures optimal nutrient extraction from the foods you consume.
Supporting a Healthy Gut Microbiome
Probiotics introduce beneficial bacteria to the gut, supplementing the existing microbial community. This can help rebalance an imbalanced microbiome, potentially reducing the presence of harmful bacteria. The addition of prebiotics, which serve as food for beneficial bacteria, further supports the growth and activity of these beneficial microbes. This combination of probiotics and prebiotics creates a synergistic effect for a healthier gut microbiome.
Link Between Gut Health and Chronic Diseases
Emerging research suggests a strong correlation between gut health and chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and even certain types of cancer. A dysbiotic gut microbiome, characterized by an imbalance in the types of gut bacteria, might contribute to the development and progression of these conditions. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome through probiotics and prebiotics could potentially reduce the risk of these chronic conditions.
Reducing Inflammation in the Gut
Probiotics can help modulate the inflammatory response in the gut. They can produce anti-inflammatory compounds and promote the growth of beneficial bacteria that suppress inflammation. A reduction in inflammation in the gut can improve overall digestive health and potentially reduce the risk of various diseases. Maintaining a healthy gut environment through probiotics could potentially alleviate symptoms of inflammatory conditions.
Summary Table of Probiotic Benefits
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Improved Digestion | Enhanced nutrient absorption, reduced digestive discomfort |
| Immune System Support | Strengthened immune response, reduced risk of illness |
| Mental Well-being | Potential positive influence on mood and cognitive function |
| Nutrient Absorption | Production of enzymes for nutrient breakdown |
| Healthy Gut Microbiome | Rebalancing gut bacteria, promoting beneficial microbes |
| Chronic Disease Prevention | Potential reduction in risk of conditions like IBD, type 2 diabetes |
| Reduced Gut Inflammation | Modulation of inflammatory response |
Choosing the Right Probiotics and Products
Navigating the probiotic world can feel like wading through a sea of confusing claims and cryptic ingredients. But don’t worry, we’ve got you covered. Choosing the right probiotic supplement isn’t about blindly grabbing the first one you see; it’s about understanding what to look for and how to make informed decisions that support your gut health journey. Let’s dive in and demystify the process!
Choosing a probiotic is more than just picking a pretty label. It’s about selecting a product that aligns with your specific needs and goals. This involves understanding the factors that influence probiotic effectiveness and ensuring you’re making a conscious, informed choice. We’ll unpack the crucial elements to consider, from the specific strains to the dosage, helping you feel confident in your probiotic journey.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Probiotic Supplements
Probiotic supplements aren’t one-size-fits-all. Factors like your age, health conditions, and dietary preferences play a significant role in finding the right fit. For instance, a probiotic formulated for digestive support might differ from one designed for immune health. Understanding your needs is key. Also, consider the strain types and the amount of live bacteria in the product.
Checking Product Labels for Quality and Potency
When evaluating probiotic supplements, always scrutinize the product label. It’s your roadmap to understanding the product’s quality and potency. Look for specifics like the CFU (Colony Forming Units) count per serving. A higher CFU count generally indicates a greater concentration of live bacteria, potentially leading to a more pronounced effect. Also, look for third-party certifications, like those from organizations that ensure the product’s quality and safety. These certifications can be a valuable indicator of the manufacturer’s commitment to quality control.
Probiotic Dosage and Duration of Use
Probiotic dosages vary greatly, depending on the product and the specific needs of the individual. There’s no universal “right” amount, but generally, a product containing a recommended daily dose of 10 billion to 50 billion CFUs is a common range. Remember, the product information should clearly state the optimal dosage for maximum benefit. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations. The duration of use also varies. Some individuals experience noticeable benefits within a few weeks, while others may need to continue use for several months. Be patient and consistent.
Potential Interactions with Medications
Probiotics can sometimes interact with certain medications. For example, some medications can alter the absorption or effectiveness of probiotics. Antibiotics are a significant example, as they can negatively impact the gut microbiome. Always discuss the potential interactions with your doctor before starting any new probiotic regimen. If you’re on medication, consulting your doctor or pharmacist is crucial to prevent potential complications.
Comparison of Different Probiotic Brands
| Brand | Key Features | CFUs per Serving |
|—————-|—————————————————————————————————————————————————|——————-|
| Probiotic A | Formulated for digestive health, includes specific strains known for their impact on gut flora, third-party certified for quality assurance | 25 billion |
| Probiotic B | Supports immune function, includes strains known for immune-boosting properties, comes in a convenient capsule format | 10 billion |
| Probiotic C | Suitable for vegans, utilizes plant-based delivery systems, and focuses on promoting overall gut health | 50 billion |
*Note: This is a sample table. Always consult product labels for precise details and compare various brands.*
Consulting a Healthcare Professional Before Starting a Probiotic Regimen
Before incorporating probiotics into your routine, consulting a healthcare professional is highly recommended. This is especially true if you have underlying health conditions, are taking medications, or are pregnant or breastfeeding. A healthcare professional can assess your individual needs and recommend the most suitable probiotic supplement, dosage, and duration. This ensures that you are making an informed choice that aligns with your overall health goals.
Addressing Common Concerns
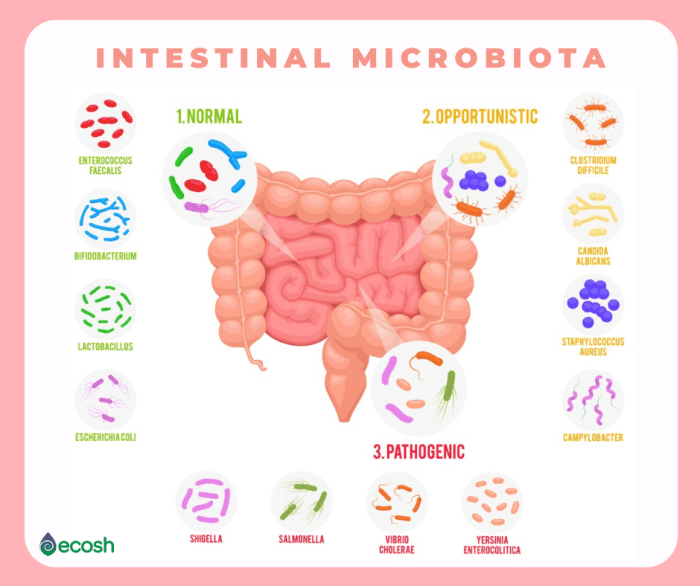
Source: ecosh.com
Probiotics, while generally safe, aren’t a magic bullet for digestive woes. Like any supplement, they come with potential downsides and considerations. Understanding these aspects helps you make informed choices and navigate any issues that might arise. So, let’s delve into the potential drawbacks and how to manage them effectively.
Potential Drawbacks and Risks of Probiotics
Probiotics, though beneficial, can sometimes cause mild side effects, especially in the initial stages of consumption. These may include bloating, gas, or diarrhea. These are often temporary and resolve as your gut adjusts to the new bacteria. Rarely, severe allergic reactions or interactions with existing health conditions can occur. Always consult a healthcare professional before introducing probiotics, particularly if you have underlying medical conditions or are taking other medications. Furthermore, some strains of probiotics might not be suitable for everyone, and choosing the right strain is crucial for individual needs.
Managing Common Side Effects
Starting with a low dose of probiotics and gradually increasing it can help mitigate potential side effects. Drinking plenty of water and adjusting your diet to incorporate easily digestible foods can also lessen the impact. If side effects persist or worsen, discontinue use and consult a healthcare professional immediately. Listening to your body’s signals is essential when introducing any new supplement.
The Importance of a Balanced Diet for Optimal Gut Health
A healthy gut isn’t just about probiotics; it’s a holistic approach. A balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables is fundamental to fostering a thriving gut microbiome. Fiber acts as fuel for beneficial bacteria, while a variety of nutrients ensures a diverse ecosystem. Limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive alcohol consumption is also vital for a healthy gut environment. The right foods can significantly impact gut health, making it a crucial element in a healthy lifestyle.
The Role of Stress Management in Maintaining Digestive Health
Chronic stress can disrupt the delicate balance of the gut microbiome. Stress hormones can negatively impact digestive processes, potentially leading to discomfort and issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Stress management techniques like meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature can help maintain a healthy gut. Finding healthy coping mechanisms for stress is essential to overall well-being, including digestive health.
Questions to Ask a Healthcare Professional About Probiotics
Before starting any probiotic regimen, it’s essential to discuss your individual needs with a healthcare professional. Consider these questions:
- What are the potential risks and benefits of taking probiotics based on my specific health conditions?
- Which probiotic strains are best suited for my needs?
- What dosage and duration of use is recommended for me?
- Are there any potential interactions with my current medications?
- What are the warning signs that indicate I should discontinue use?
These questions can ensure you’re making an informed decision about probiotics and address any concerns.
Potential Probiotic Interactions with Medications
Probiotics can interact with certain medications, potentially altering their absorption or effectiveness. Careful consideration is needed when taking probiotics alongside specific medications. Consulting with a doctor or pharmacist is crucial to understand these potential interactions.
| Medication | Potential Interaction |
|---|---|
| Antibiotics | May affect the effectiveness of certain antibiotics. |
| Immunosuppressants | May affect immune response. |
| Blood thinners | May affect blood clotting. |
| Acid reducers | May affect the effectiveness of probiotics. |
This table provides a general overview; specific interactions can vary depending on the individual and the medications involved. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Case Studies and Research
Unveiling the science behind probiotics and gut health involves delving into a world of fascinating research and case studies. From understanding how different diets impact our gut microbiome to exploring the various research methods employed, the journey to better gut health is paved with evidence-based insights. This section will explore the latest findings, successful applications, and the ongoing challenges in the field.
Recent Research Findings on Probiotics and Gut Health
Recent research has illuminated the complex relationship between probiotics and various health conditions. Studies have shown promising results in alleviating symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and improving immune function. Furthermore, research suggests probiotics may play a role in reducing the risk of certain infections and even impacting mental well-being. Specific strains of probiotics have demonstrated particular efficacy in targeting specific conditions. For instance, certain strains have shown potential in reducing inflammation and enhancing nutrient absorption.
Examples of Successful Case Studies on the Use of Probiotics
Numerous case studies highlight the potential benefits of probiotics. One notable example involves a group of individuals with IBS experiencing significant improvements in their digestive symptoms after incorporating specific probiotic strains into their daily routine. Similarly, case studies have shown improvements in the regularity and comfort of bowel movements in those with chronic constipation. These studies underscore the potential of probiotics as a complementary therapy for various digestive issues.
Impact of Different Diets on Gut Microbiota Composition
Dietary choices significantly impact the composition of the gut microbiota. A diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables, often referred to as a “gut-friendly” diet, fosters a diverse and balanced gut microbiome. Conversely, a diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can negatively affect the gut microbiome’s diversity. The impact of these dietary choices on gut health is a crucial area of ongoing research.
Description of Various Research Methods Used to Study Gut Health
Researchers utilize various methods to study gut health, including fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), metagenomics, and 16S rRNA sequencing. FMT involves transferring fecal material from a healthy donor to a recipient, often used to treat recurrent Clostridium difficile infections. Metagenomics analyzes the entire genetic material of the gut microbiota, providing a comprehensive view of its composition. 16S rRNA sequencing targets specific genes in bacteria to identify the different bacterial species present in the gut. These methods, along with others, allow scientists to gather a wealth of data about the intricacies of gut health.
Summary of Key Research Findings on Probiotics and Their Applications
| Probiotic Strain | Condition | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus acidophilus | Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) | Some studies show improvements in IBS symptoms, particularly abdominal pain and bloating. |
| Bifidobacterium bifidum | Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) | Preliminary research suggests potential benefits in reducing inflammation in some cases. |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus | Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea | Demonstrates a potential to reduce the risk of antibiotic-associated diarrhea. |
Limitations of Existing Research on Probiotics
Current research on probiotics faces limitations. The diverse nature of gut microbiota, along with variations in individual responses to probiotics, presents significant challenges in drawing definitive conclusions. Furthermore, long-term studies are often lacking, and standardization in probiotic product formulation and dosage is necessary for robust comparisons. These factors contribute to the complexity of understanding the full impact of probiotics on human health.
Summary
Source: org.uk
In conclusion, Digestive Health: Probiotics and Gut-Friendly Products has shown us the profound connection between our gut and overall health. We’ve explored the world of probiotics, the power of gut-friendly foods, and the benefits they bring to our well-being. By understanding the importance of a balanced diet, stress management, and the right probiotic choices, you can unlock a healthier, happier gut. Armed with this knowledge, you’re empowered to take control of your digestive health and achieve optimal well-being.