Sun Protection Smarts: The Best SPF Products for All Seasons. Seriously, sun protection isn’t just for summer. From the scorching rays of summer to the sneaky spring showers, and even the crisp air of fall and winter, UV rays are always lurking, ready to wreak havoc on your skin. This guide breaks down everything you need to know about choosing the right SPF for every season, every skin type, and every activity. Get ready to shield your skin with smart sun protection strategies.
We’ll explore the science behind SPF ratings, uncover the best products for different skin types and activities, and even dive into the environmental impact of your sunscreens. Arm yourself with the knowledge to protect your skin all year round. From understanding UV rays to applying your sunscreen like a pro, this is your ultimate sun protection resource.
Sun Protection Smarts
Hey there, sun-worshippers! We all love soaking up the rays, but did you know that sun protection isn’t just for summer? It’s a year-round commitment for healthy skin, and understanding the different types of UV rays is key to keeping your complexion glowing and vibrant, no matter the season. Let’s dive into the essentials of sun protection and discover the best SPF products for every day.
Protecting your skin from the sun’s harmful rays is crucial for maintaining its health and beauty. Sun exposure, even on cloudy days, can lead to premature aging, wrinkles, and an increased risk of skin cancer. Consistent sun protection, coupled with a healthy lifestyle, is the best way to keep your skin looking its best for years to come.
Understanding UV Rays
The sun emits different types of ultraviolet (UV) radiation, and both UVA and UVB rays can cause damage to the skin. UVA rays penetrate deeply into the skin, contributing to long-term damage like wrinkles and age spots. UVB rays are more potent at causing sunburn, but they also play a role in premature aging and skin cancer.
The Importance of Year-Round SPF
Sun protection isn’t just for the beach. Even on overcast days, UV rays can still reach your skin. This means you need to wear sunscreen every day, regardless of the weather. Think of it as an essential part of your skincare routine, like moisturizing.
Choosing the Right SPF for Your Needs
The ideal SPF for you depends on your skin type, the amount of sun exposure you’re likely to experience, and the time of year. A higher SPF provides greater protection, but it’s not always necessary to choose the highest available. For example, a daily SPF 30 can effectively shield your skin from most of the sun’s harmful rays.
Different Types of Sunscreen
Different sunscreen formulations offer different benefits. Some sunscreens are specifically designed for sensitive skin, while others are water-resistant or broad-spectrum. Understanding the different types available can help you choose the best sunscreen for your needs.
Applying Sunscreen Correctly
Applying sunscreen correctly is just as important as choosing the right product. A general guideline is to apply a generous amount of sunscreen, at least 15-30 minutes before sun exposure. Reapply every two hours, or more frequently if you’re swimming or sweating.
Beyond Sunscreen: Additional Protective Measures
Wearing protective clothing, such as hats and sunglasses, can also significantly reduce your exposure to harmful UV rays. Seeking shade during peak sun hours is another great way to safeguard your skin from sun damage. For example, if you’re spending a lot of time outdoors, consider taking breaks in the shade to minimize sun exposure.
Understanding SPF Ratings
SPF, or Sun Protection Factor, is a crucial number that tells you how well a sunscreen protects your skin from the sun’s harmful UVB rays. It’s a fundamental aspect of sun protection, but understanding *how* it works is key to choosing the right product for your needs. Knowing the nuances of SPF ratings allows you to make informed decisions about your daily sun safety routine.
SPF ratings aren’t just arbitrary numbers; they represent a calculated comparison of how long you can stay in the sun with sunscreen compared to how long you can stay without it. Essentially, a higher SPF means longer sun protection. This understanding empowers you to choose sunscreens that offer the best defense against sunburn and the long-term damage of UV exposure.
How SPF Ratings Work
SPF ratings quantify the degree of protection a sunscreen provides against UVB radiation. A higher SPF means longer sun exposure before sunburn. For example, an SPF 30 sunscreen theoretically allows you to stay in the sun 30 times longer without getting burned compared to when you’re not wearing sunscreen. It’s important to remember this is a theoretical maximum, and actual protection depends on many factors.
Different Ways SPF Ratings Are Measured and Tested
SPF ratings are determined through standardized testing procedures. These tests typically involve measuring how much UVB radiation a specific sunscreen absorbs and how this absorption affects the skin’s reaction to UV exposure. The tests are conducted under controlled laboratory conditions to ensure accurate and consistent results. The standardized test conditions help consumers compare sunscreen products fairly and consistently.
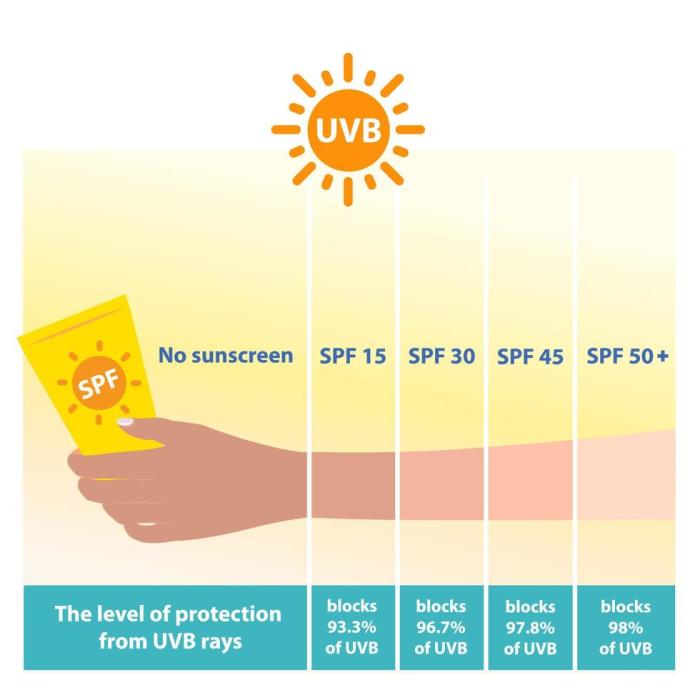
Comparison of SPF Ratings and Their Effectiveness
Different SPF ratings offer varying levels of protection. An SPF 15 sunscreen filters out about 93% of UVB rays, while an SPF 30 sunscreen blocks about 97%. The difference in protection between SPF 15 and SPF 30 is significant, but the increment in protection from SPF 30 to SPF 50 or higher is less pronounced. For everyday use, SPF 30 is generally considered sufficient for most people. However, those with light skin or higher sun sensitivity may benefit from higher SPF ratings.
Broad-Spectrum Protection
Sunscreens offering broad-spectrum protection shield your skin from both UVA and UVB rays. UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin and are linked to premature aging and long-term skin damage. Broad-spectrum sunscreens are crucial for comprehensive sun protection, as they address both types of harmful UV radiation. Look for labels that explicitly state “broad-spectrum” or “UVA/UVB protection” to ensure you’re getting this comprehensive protection.
Choosing the Right SPF for Different Skin Types
Source: vecteezy.com
Sunscreen is crucial, but did you know taking care of your smile is equally important? Just like choosing the right SPF for your skin, upgrading your oral health routine, like flossing more often and visiting the dentist regularly, is key. Check out Oral Health Essentials: Upgrading Your Dental Routine for some top tips. Ultimately, prioritizing both your skin and your mouth leads to a healthier, happier you – and remember to slather on that SPF, even on cloudy days!
Knowing your skin type is crucial for effective sun protection. Different skin types react differently to the sun’s harmful UV rays, and understanding these variations helps you choose the right SPF for optimal sun safety. This knowledge empowers you to select products tailored to your individual needs, minimizing the risk of sunburn and long-term skin damage.
Skin type significantly influences your sun sensitivity. Some skin types are more prone to burning, while others might be more susceptible to tanning or premature aging. This sensitivity difference underscores the importance of personalized sun protection strategies.
Skin Type Classification
Skin types are broadly categorized based on their pigmentation and tendency to burn or tan. This categorization provides a general framework for understanding individual sun sensitivity.
- Type I (Very Fair): This skin type is often pinkish or red and burns easily, tanning minimally or not at all. Individuals with this skin type are highly sensitive to UV rays and require the highest SPF protection.
- Type II (Fair): This skin type tends to be light to medium in color, often with a tendency to burn. Tanning occurs slowly, but it’s crucial to use a high SPF.
- Type III (Light): This skin type is typically light brown or medium in color. It burns less easily than the previous two types but still requires a substantial SPF level.
- Type IV (Medium): This skin type is usually medium to deep brown. It tans easily and burns less frequently. A medium to high SPF is generally adequate.
- Type V (Deep): This skin type is typically dark brown to black. It tans easily and burns less often. A medium to lower SPF is usually suitable, though it’s essential to apply sunscreen regularly to prevent damage.
- Type VI (Very Dark): This skin type is typically very dark brown or black. It’s the least sensitive to sunburns, but sunscreen application remains essential to prevent premature aging and skin damage.
Factors Affecting Sun Sensitivity
Beyond skin type, several other factors influence your sun sensitivity.
- Medications: Some medications can increase your skin’s sensitivity to the sun. This effect is often temporary and is often listed as a side effect in the medicine’s description.
- Freckles and Moles: Areas with freckles or moles are often more prone to sun damage. These areas require increased attention and higher SPF products.
- Sun Exposure History: Past sunburns can increase your skin’s sensitivity to future sun exposure. Regular application of sunscreen is crucial, even after recovering from sunburns.
- Altitude: Higher altitudes often mean increased UV radiation, requiring higher SPF protection.
- Time of Day: UV rays are strongest during midday, making it essential to use a high SPF during these hours.
Choosing the Right SPF Product
Consider these factors when selecting SPF products:
- Broad-Spectrum Protection: Look for sunscreens that protect against both UVA and UVB rays. This dual protection is essential for comprehensive sun protection.
- Water Resistance: Choose water-resistant sunscreen if you’ll be swimming or sweating. Re-application is crucial to maintain protection.
- Skin Type Compatibility: Select a sunscreen formulated for your skin type to avoid irritation or other adverse reactions. Check for ingredients like fragrance and other additives, which can sometimes trigger skin reactions.
- Ingredients: Familiarize yourself with the ingredients and their potential benefits. Some ingredients offer additional benefits like antioxidants or moisturizers.
Seasonal Sun Protection Considerations
The sun’s intensity and the amount of time we spend outdoors fluctuate dramatically throughout the year. Understanding these seasonal variations is key to maintaining optimal sun protection and safeguarding your skin from harmful UV rays. This knowledge allows you to choose the right SPF for the specific conditions you’ll encounter.
Seasonal changes in weather patterns and daylight hours directly impact our sun exposure. This means your skin’s need for protection shifts as the calendar turns, from the intense summer sun to the colder, but still potentially harmful, winter rays.
Summer Sun Protection
Summer brings longer days and higher temperatures, leading to increased sun exposure. The sun’s rays are stronger, and the risk of sunburn is significantly higher. Proper sun protection is essential to prevent damage and maintain healthy skin.
- Increased UV exposure: Longer daylight hours and higher sun angles result in more direct and intense UV radiation. This makes it crucial to shield your skin from the sun’s harmful effects.
- Higher risk of sunburn: The intensity of the summer sun significantly elevates the likelihood of sunburn, which can lead to painful skin damage and increase the risk of long-term skin problems.
- Suitable SPF products: Look for broad-spectrum SPFs with an SPF of 30 or higher for everyday use. Water-resistant formulas are ideal for activities like swimming and outdoor sports. Choose formulas that feel light and don’t clog pores.
Spring Sun Protection
As daylight hours lengthen and temperatures rise, the sun’s intensity increases, requiring appropriate sun protection measures.
- Transitional exposure: Spring often brings a transition period in sunlight intensity and duration, requiring adaptable sun protection. Skin may be more sensitive after the winter months.
- Increased outdoor activities: With warmer weather, people are more likely to spend time outdoors, engaging in activities like gardening, picnics, and sporting events. This necessitates consistent sun protection.
- Suitable SPF products: A broad-spectrum SPF of 30 or higher is recommended for spring. Choose a lightweight, non-greasy formula to suit your needs.
Fall Sun Protection
Autumn marks a gradual shift in weather conditions and daylight hours. The sun’s intensity begins to decrease, but protection is still vital.
- Decreased intensity: While the sun’s intensity is generally lower in fall compared to summer, it still poses a risk of sunburn, especially during midday hours.
- Outdoor activities continue: People are still likely to engage in outdoor activities, such as hiking, apple picking, or attending outdoor events. Protecting your skin from UV rays remains important.
- Suitable SPF products: An SPF of 15 to 30, depending on your skin type and activity level, is appropriate for fall. Choose a lightweight lotion or spray to easily apply.
Winter Sun Protection
Despite the shorter daylight hours and colder temperatures, the sun’s rays can still cause damage during winter.
- Reflected UV rays: Snow and ice reflect UV rays, increasing the amount that reaches your skin. Even on cloudy days, UV radiation can penetrate the atmosphere.
- Reduced exposure time, but not reduced risk: While the amount of direct sunlight is less than in summer, the risk of damage remains significant, especially during midday hours when the sun’s rays are more intense.
- Suitable SPF products: An SPF of 15 to 30, depending on your skin type and activity level, is recommended for winter. Choose a moisturizing formula to combat dryness.
SPF Product Types and Features
Sunscreen comes in various forms, each with its own pros and cons. Understanding these differences is key to choosing the best protection for your needs, whether you’re lounging by the pool or tackling a brisk hike. The right product type can significantly improve your application experience and ensure you’re truly maximizing your SPF protection.
Choosing the right sunscreen depends on factors like your skin type, lifestyle, and even the weather. For example, a lotion might be ideal for everyday use, while a spray might be more convenient for reapplication during outdoor activities. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each type helps you pick the perfect match for your sun-safe adventures.
SPF Product Types
Different sunscreen formats cater to various preferences and needs. The type you choose should align with your lifestyle and application comfort.
- Lotions: Lotions are a common and versatile sunscreen type. They typically have a lighter consistency, making them easy to apply and absorb quickly into the skin. This characteristic makes them suitable for daily use, blending seamlessly into your routine.
- Creams: Creams are often thicker and richer than lotions, offering a more substantial layer of protection. They are particularly beneficial for individuals with dry or sensitive skin, providing a more moisturizing experience. The extra coverage is perfect for those seeking an extra barrier against the sun’s harsh rays.
- Sprays: Sprays offer a convenient method for quick application, especially for large areas or when reapplying during outdoor activities. However, they can be challenging to apply evenly and may not provide complete coverage in some areas. Proper technique and multiple passes are often necessary to ensure sufficient protection.
- Sticks: Sunscreen sticks are excellent for targeted application on specific areas, like the nose, ears, or lips. They are also useful for touch-ups and provide a concentrated dose of protection where it’s needed most. This targeted approach is invaluable for maintaining consistent SPF throughout the day.
Water and Sweat Resistance
Water and sweat resistance are crucial factors to consider, especially for outdoor activities. The ability of a sunscreen to withstand water and sweat is measured in terms of how long it remains effective under these conditions.
- Water Resistance: Water-resistant sunscreens are formulated to maintain their effectiveness for a specific duration when exposed to water. This is vital for activities like swimming or participating in water sports, ensuring continued protection throughout the activity. Look for products labeled with specific time frames, such as “water resistant for 40 minutes.”
- Sweat Resistance: Sweat-resistant sunscreens are designed to stay effective despite perspiration. This is particularly important for activities that involve significant sweating, like intense workouts or strenuous outdoor labor. Products labeled “sweat resistant” offer sustained protection even under conditions of increased moisture.
Comparison Table of SPF Product Types
| Type | Benefits | Drawbacks | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lotion | Easy to apply, absorbs quickly, suitable for daily use | May not provide as much coverage as creams | Apply evenly in thin layers, allowing each layer to absorb before applying more |
| Cream | Provides substantial coverage, beneficial for dry or sensitive skin | Can be thicker and take longer to absorb | Apply in thin layers and gently massage into the skin |
| Spray | Convenient for large areas and reapplication | Can be challenging to apply evenly, may not provide complete coverage | Hold the can a few inches from the skin and spray in a light, even motion |
| Stick | Excellent for targeted application, ideal for touch-ups | Limited coverage area, may not be suitable for large body areas | Apply directly to the desired area, using gentle pressure |
Active Ingredients in Sun Protection Products
Sunscreen isn’t just about slapping on a lotion; it’s about understanding the science behind the shield. Different active ingredients work in unique ways to protect your skin from the sun’s harmful rays. Knowing these ingredients and their mechanisms of action can empower you to choose the best protection for your skin type and needs.
Common Active Ingredients, Sun Protection Smarts: The Best SPF Products for All Seasons
Sunscreens rely on a variety of active ingredients to absorb, scatter, and reflect UV rays. Understanding these ingredients is key to choosing the right product for you.
Chemical Filters
Chemical filters absorb UV rays and convert them into heat, which is then released. This process helps prevent UV damage to the skin. These ingredients are often lightweight and quickly absorbed, making them popular choices for everyday use.
- Oxybenzone (Benzophenone-3): This is a widely used chemical filter that absorbs UV radiation. It works by absorbing UV-B and some UV-A rays and converting them into heat. While effective, concerns about potential environmental impact and possible skin sensitivities have led to some regulations and consumer choices.
- Octinoxate: Another popular chemical filter, octinoxate, also absorbs UV-B and some UV-A rays. It is known for its effectiveness in broad-spectrum sun protection, meaning it protects against both UVA and UVB rays.
- Avobenzone: This filter is particularly effective at absorbing UVA rays, a type of UV radiation that can penetrate deeper into the skin and cause long-term damage. Its effectiveness is often paired with other filters to provide broader protection.
- Homosalate: A chemical filter that absorbs UV-B radiation. It’s known for its relatively mild nature and is often found in formulations designed for sensitive skin.
- Octisalate: Similar to homosalate, octisalate absorbs UV-B radiation. It’s often used in combination with other chemical filters to enhance the overall protection.
Physical Filters
Physical filters, unlike chemical filters, create a physical barrier on the skin that reflects UV rays. This method is generally considered gentler on the skin and less prone to environmental concerns.
- Zinc Oxide: This mineral reflects and scatters UV radiation, creating a protective layer on the skin. Zinc oxide is a gentle option for most skin types, including sensitive skin, and is often used in sunscreens for children and those with skin sensitivities.
- Titanium Dioxide: Another mineral-based filter, titanium dioxide, also works by reflecting and scattering UV rays. It’s a popular choice for broad-spectrum sun protection and often used in combination with other ingredients for enhanced efficacy.
Active Ingredient Table
| Active Ingredient | Function | Possible Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Oxybenzone | Absorbs UV radiation, converting it to heat | Potential environmental impact, skin irritation, allergic reactions in some individuals |
| Octinoxate | Absorbs UV-B and some UV-A rays | Skin irritation, allergic reactions in some individuals |
| Avobenzone | Effective at absorbing UVA rays | Potential for skin irritation in some individuals |
| Homosalate | Absorbs UV-B radiation | Mild skin irritation in some individuals |
| Octisalate | Absorbs UV-B radiation | Mild skin irritation in some individuals |
| Zinc Oxide | Reflects and scatters UV radiation | Potential for white cast on skin |
| Titanium Dioxide | Reflects and scatters UV radiation | Potential for white cast on skin |
Application Techniques and Best Practices
Sunscreen isn’t just about slapping some lotion on; it’s about applying it *correctly* for maximum protection. Proper application technique, the right amount, and avoiding common pitfalls are crucial for getting the most out of your SPF. This section will equip you with the knowledge to confidently shield your skin from the sun’s harmful rays.
Optimal Application Methods
Proper application is key to achieving effective sun protection. A common mistake is applying too little product, which significantly reduces its effectiveness. The amount needed varies depending on the body area and size, but a general guideline is to use a shot glass-sized amount for your entire body. It’s vital to ensure every inch of exposed skin is coated. Using a sunscreen applicator or a dedicated brush can help to apply evenly. For delicate areas like the face and neck, use gentle, circular motions.
Amount Needed for Effective Protection
The amount of sunscreen required for optimal protection is often underestimated. A common misconception is that a thin layer will suffice. A sufficient amount is crucial for creating a protective barrier against UV rays. Think of it as a shield for your skin, and a thin layer is ineffective. A dime-sized amount is a great starting point for the face, but for the entire body, the amount should be more akin to a shot glass. This ensures every inch of exposed skin is adequately covered.
Common Application Mistakes
Many people unknowingly make mistakes in their sunscreen application routine, leading to inadequate protection. One common pitfall is applying sunscreen just before heading out, failing to account for the absorption time. Another is not applying enough product, which results in incomplete coverage. Forgetting to reapply sunscreen throughout the day, especially after swimming or sweating, is another significant oversight. Remember, reapplication is essential to maintain protection.
Step-by-Step Guide to Applying SPF
Applying sunscreen correctly is a simple process. Follow these steps for optimal protection:
- Start by cleansing and moisturizing your skin. This ensures the sunscreen absorbs effectively and won’t sit on top of dry patches.
- Use a shot glass-sized amount of sunscreen for the entire body. For smaller areas like the face, a dime-sized amount is sufficient.
- Apply sunscreen 15-30 minutes before sun exposure to allow for proper absorption.
- Apply liberally to all exposed skin, including the face, neck, ears, and the tops of your feet. Don’t forget areas that are frequently overlooked.
- Make sure to apply to the hairline, behind the ears, and the tops of your feet. Ensure even coverage to every part of your skin.
- Rub the sunscreen gently into the skin, ensuring it is evenly distributed. Avoid rubbing vigorously, as this can irritate the skin.
- Reapply every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
Sun Protection for Different Body Parts
Protecting your skin from the sun isn’t a one-size-fits-all affair. Different body parts experience varying degrees of sun exposure, demanding tailored sun protection strategies. Understanding these nuances ensures comprehensive sun safety for every inch of your body.
Knowing the specific sun protection needs of your face, neck, hands, and feet is key to preventing sunburn and long-term skin damage. This tailored approach is crucial for maintaining healthy skin across your entire body.
Face: The Spotlight of Sun Exposure
The face, constantly exposed to the sun’s rays, requires particularly strong sun protection. Sun damage on the face often manifests as premature aging, wrinkles, and dark spots. Using a broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher is essential for daily protection. Look for lightweight formulas that won’t clog pores. Consider a tinted moisturizer or a mineral sunscreen for added benefits and coverage. For extra protection, consider a hat or visor. For example, La Roche-Posay Anthelios Melt-In Sunscreen Milk SPF 60 is a popular choice for facial protection.
Neck: The Often-Forgotten Zone
The neck, frequently overlooked, is susceptible to the same sun damage as the face. The delicate skin on the neck is prone to wrinkles and discoloration. Applying the same high SPF product to the neck as you do to your face is crucial. Don’t forget to include the front, back, and sides of your neck in your application routine. A daily SPF 30+ is vital. For instance, EltaMD UV Clear Broad-Spectrum SPF 46 is a good option, known for its gentle formula suitable for sensitive skin.
Hands: The Daily Workhorses
Hands are exposed to the sun throughout the day, especially during outdoor activities. The skin on hands is often thinner and more prone to dryness and cracking. Choose a water-resistant SPF 30+ sunscreen for hands to protect them from the elements. Look for products with moisturizing ingredients. Apply liberally, and reapply frequently, particularly after swimming or sweating. For instance, Supergoop! Unseen Sunscreen SPF 40 is a popular choice known for its lightweight texture and broad-spectrum protection.
Feet: The Often-Ignored Areas
Feet are often overlooked when it comes to sun protection. However, the skin on the feet, particularly the tops, can get sunburned, especially in the summer months. Apply a generous amount of sunscreen, especially to the tops and sides of the feet, to prevent sunburn. Water-resistant formulas are highly recommended, especially if you spend time near water. Choose a moisturizing sunscreen specifically designed for feet. For example, CeraVe AM Facial Moisturizing Lotion with SPF 30 is suitable for feet.
Comparing Sun Protection Needs and Suitable Products
| Body Part | Sun Exposure Level | Recommended SPF | Example Product |
|---|---|---|---|
| Face | High | 30+ | La Roche-Posay Anthelios Melt-In Sunscreen Milk SPF 60 |
| Neck | High | 30+ | EltaMD UV Clear Broad-Spectrum SPF 46 |
| Hands | Moderate to High | 30+ (water-resistant) | Supergoop! Unseen Sunscreen SPF 40 |
| Feet | Moderate | 30+ (water-resistant) | CeraVe AM Facial Moisturizing Lotion with SPF 30 |
Sun Protection for Children and Infants
Protecting little ones from the sun’s harmful rays is crucial for their long-term health. Children’s skin is thinner and more sensitive than adults’, making them more susceptible to sunburn and long-term skin damage. Proper sun protection strategies are essential to prevent these issues and ensure their safety during outdoor activities.
Sun exposure during childhood can significantly increase the risk of skin cancer later in life. Implementing effective sun protection measures early on can help mitigate this risk. This is why focusing on sun protection for children and infants is a critical aspect of overall health and well-being.
Specific Sun Protection Products for Children
Formulating sun protection products for children requires careful consideration of their unique needs. Children’s skin is often more sensitive and prone to irritation than adults’, so products designed specifically for children utilize gentler ingredients and formulations. These products are typically hypoallergenic and free of harsh chemicals, minimizing the risk of allergic reactions. They are also often fragrance-free, further reducing the chance of skin irritation. Choosing products designed for children ensures a safer and more comfortable experience.
Importance of SPF Ratings for Children
Children require the same level of sun protection as adults. The SPF rating of a sunscreen indicates its effectiveness in blocking ultraviolet (UV) radiation. A higher SPF rating provides greater protection. Children, especially infants, should use sunscreens with a high SPF rating, typically SPF 30 or higher. Using products with a high SPF is essential to shield their delicate skin from harmful UV rays. Remember that even on cloudy days, the sun’s harmful rays can penetrate the clouds and cause damage.
Supervised Sun Exposure for Children
Constant supervision and monitoring of sun exposure are crucial for children, especially infants. Keeping infants shaded under umbrellas, protective clothing, and seeking shade during peak sun hours are crucial. Regular breaks in the sun are important to prevent overexposure, especially for infants who have limited ability to self-regulate their sun exposure. Parents and caregivers should always be vigilant in ensuring that children are not exposed to the sun for extended periods, particularly during midday hours when the sun’s rays are strongest. Taking frequent breaks and ensuring proper hydration are essential.
Sun Protection for Infants
Infants, particularly those with lighter skin tones, require extra protection from the sun. Infants’ skin is more sensitive and prone to sunburn. Using a dedicated infant sunscreen, often formulated with mineral-based sunscreens, can help protect them. These sunscreens are usually gentle on their delicate skin. Avoid applying sunscreen directly to a baby’s face. Instead, apply it to the surrounding areas of the face, and then gently pat it into the skin. This helps prevent irritation.
Environmental Considerations
Protecting our skin from the sun is crucial, but so is protecting our planet. Choosing sunscreens that minimize harm to marine ecosystems and the environment as a whole is becoming increasingly important. This section delves into the environmental impact of different sunscreens, highlighting reef-safe ingredients and the importance of sustainable practices.
The chemical cocktail in many sunscreens is now recognized as a threat to marine life, coral reefs, and the delicate balance of our oceans. Understanding the ingredients and their potential impact is essential for making informed choices that benefit both our health and the environment.
Environmental Impact of SPF Products
Sunscreens, while vital for sun protection, can have significant environmental consequences if not carefully formulated. Microplastics, chemical filters, and other ingredients can pollute water bodies, impacting aquatic life. The impact varies depending on the specific ingredients used.
Reef-Safe Ingredients
Many sunscreens contain chemicals that are harmful to coral reefs and other marine life. Thankfully, there are now alternatives that are safer for coral reefs. These “reef-safe” ingredients are formulated to avoid harming delicate marine ecosystems.
- Oxybenzone and octinoxate are two common chemicals frequently found in sunscreens that are known to be harmful to coral reefs. These chemicals can disrupt coral reproduction and growth, and cause damage to other marine organisms. Luckily, there are now several alternative ingredients that have been shown to be safer for the environment.
- Zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are considered reef-safe alternatives to oxybenzone and octinoxate. These mineral-based filters are generally considered less harmful to coral reefs and other marine organisms. Their physical properties reflect UV rays rather than absorbing them, thus causing less disruption to the delicate balance of the marine ecosystem.
Importance of Sustainable Sun Protection
Sustainable sun protection goes beyond choosing reef-safe ingredients. It encompasses the entire lifecycle of the product, from sourcing materials to packaging and disposal. The goal is to minimize the environmental footprint of sunscreen use. Eco-friendly packaging, recyclable containers, and ethical sourcing practices are key aspects of sustainable sun protection.
Pros and Cons of Different Ingredients
Different ingredients in sunscreens have varying impacts on the environment. Careful consideration of the pros and cons of each ingredient is crucial for making informed choices.
| Ingredient | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Zinc Oxide | Generally considered reef-safe, biodegradable, and non-toxic. | Can sometimes leave a white cast on the skin. |
| Titanium Dioxide | Similar benefits to zinc oxide, considered reef-safe, biodegradable, and non-toxic. | Can sometimes leave a white cast on the skin. |
| Oxybenzone | Effective at blocking UV rays. | Known to harm coral reefs and other marine life. |
| Octinoxate | Effective at blocking UV rays. | Known to harm coral reefs and other marine life. |
“Choosing reef-safe sunscreens is a crucial step in protecting both our skin and the delicate ecosystems of our oceans.”
Epilogue: Sun Protection Smarts: The Best SPF Products For All Seasons
So, there you have it—a comprehensive look at mastering sun protection year-round. Remember, sun protection isn’t just about applying sunscreen, it’s about understanding your skin, the seasons, and the best ways to shield yourself from the sun’s harmful rays. With the right knowledge and products, you can confidently embrace the sun while keeping your skin healthy and happy, all year long. Now go forth and conquer the sun safely!